What are "ejemplos de atomos y moleculas"?
"Ejemplos de atomos y moleculas" is a Spanish phrase that means "examples of atoms and molecules." Atoms are the basic units of matter, and molecules are groups of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds. Atoms and molecules are the building blocks of all matter in the universe.
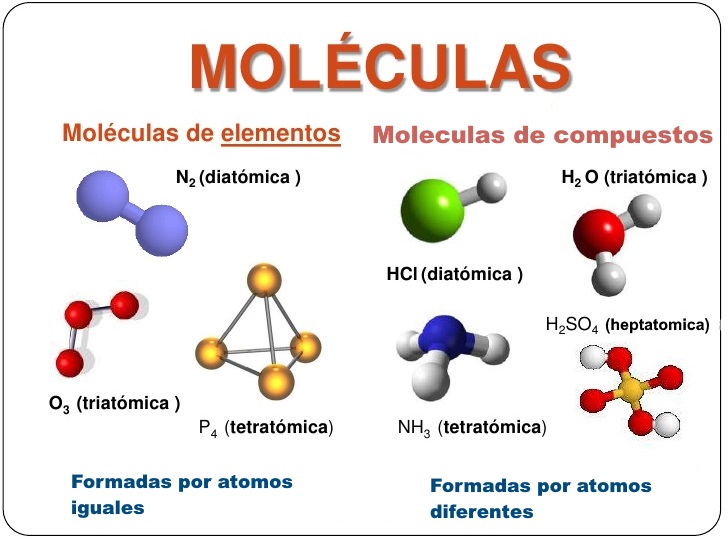
There are many different types of atoms and molecules. Some of the most common atoms include hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen. Some of the most common molecules include water, carbon dioxide, and methane.
Atoms and molecules are essential for life. Atoms make up the cells of our bodies, and molecules provide us with energy and help us to function. Without atoms and molecules, life would not be possible.
The study of atoms and molecules is called chemistry. Chemistry is a vast and complex field, but it is also a fascinating one. By studying chemistry, we can learn more about the world around us and how it works.
Ejemplos de atomos y moleculas
Atoms and molecules are the basic building blocks of all matter in the universe. They are essential for life and play a vital role in many different processes in our bodies and the world around us. Here are seven key aspects of atoms and molecules that are essential to understanding their importance:
- Structure: Atoms are composed of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, and electrons, which orbit the nucleus. Molecules are formed when two or more atoms are chemically bonded together.
- Properties: The properties of atoms and molecules are determined by the number and arrangement of their constituent particles. For example, the number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which in turn determines its chemical properties.
- Reactivity: Atoms and molecules can react with each other to form new substances. The reactivity of an atom or molecule is determined by its electronic structure.
- Energy: Atoms and molecules can absorb and release energy in the form of photons. The energy of a photon is determined by its wavelength.
- Bonding: Atoms and molecules can be bonded together by covalent bonds, ionic bonds, or hydrogen bonds. The type of bond that is formed depends on the electronegativity of the atoms involved.
- Polarity: Atoms and molecules can be polar or nonpolar. Polar atoms and molecules have a separation of charge, while nonpolar atoms and molecules do not.
- Applications: Atoms and molecules are used in a wide variety of applications, including energy production, medicine, and materials science.
These seven key aspects of atoms and molecules provide a basic understanding of their importance and role in the world around us. By understanding these aspects, we can better appreciate the complexity and beauty of the natural world.
Structure
The structure of atoms and molecules is fundamental to understanding their properties and behavior. The nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons, while electrons orbit the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which in turn determines its chemical properties. Molecules are formed when two or more atoms are chemically bonded together. The type of bond that is formed depends on the electronegativity of the atoms involved.
- Components: The basic components of atoms and molecules are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit the nucleus.
- Examples: Hydrogen is the simplest atom, consisting of one proton and one electron. Water is a simple molecule, consisting of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
- Implications: The structure of atoms and molecules determines their properties and behavior. For example, the number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which in turn determines its chemical properties.
Understanding the structure of atoms and molecules is essential for understanding the world around us. Atoms and molecules are the building blocks of all matter, and their structure determines their properties and behavior. By understanding the structure of atoms and molecules, we can better understand the world around us.
Properties
The properties of atoms and molecules are essential for understanding their behavior and interactions. For example, the number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which in turn determines its chemical properties. This is because the number of protons in an atom determines the number of electrons that the atom can hold, which in turn determines the atom's ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms.
The arrangement of atoms and molecules also plays a role in determining their properties. For example, the shape of a molecule can affect its polarity, which in turn can affect its solubility and other properties. The arrangement of atoms and molecules can also affect their reactivity, which is their ability to undergo chemical reactions with other atoms or molecules.
Understanding the properties of atoms and molecules is essential for understanding the world around us. Atoms and molecules are the building blocks of all matter, and their properties determine the behavior and interactions of all matter. By understanding the properties of atoms and molecules, we can better understand the world around us and develop new technologies.
Reactivity
The reactivity of atoms and molecules is a key aspect of their behavior and interactions. Atoms and molecules can react with each other to form new substances, and the reactivity of an atom or molecule is determined by its electronic structure. This is because the electronic structure of an atom or molecule determines its ability to gain or lose electrons, which in turn determines its ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms or molecules.
For example, atoms with a low ionization energy are more likely to react with other atoms or molecules to form new substances. This is because it is easier to remove an electron from an atom with a low ionization energy. Similarly, atoms with a high electronegativity are more likely to react with other atoms or molecules to form new substances. This is because atoms with a high electronegativity have a strong attraction for electrons.
The reactivity of atoms and molecules is also affected by their size and shape. For example, smaller atoms and molecules are more likely to react with other atoms or molecules than larger atoms and molecules. This is because smaller atoms and molecules have a higher surface area to volume ratio, which means that they have more contact with other atoms or molecules.
Understanding the reactivity of atoms and molecules is essential for understanding the world around us. Atoms and molecules are the building blocks of all matter, and their reactivity determines the behavior and interactions of all matter. By understanding the reactivity of atoms and molecules, we can better understand the world around us and develop new technologies.
Energy
The study of atoms and molecules is essential to understanding the world around us. Atoms and molecules are the building blocks of all matter, and their interactions with energy are responsible for many of the phenomena that we observe in the world around us.
- Energy Levels: Atoms and molecules have specific energy levels that they can occupy. When an atom or molecule absorbs energy, it moves to a higher energy level. When an atom or molecule releases energy, it moves to a lower energy level.
- Photons: Atoms and molecules can absorb and release energy in the form of photons. A photon is a particle of light that has a specific energy. The energy of a photon is determined by its wavelength.
- Spectroscopy: The study of the absorption and emission of light by atoms and molecules is called spectroscopy. Spectroscopy can be used to identify atoms and molecules, and to study their structure and properties.
- Applications: The principles of atomic and molecular energy are used in a wide variety of applications, including lasers, solar cells, and medical imaging.
The study of atoms and molecules is a vast and complex field, but it is also a fascinating one. By understanding the interactions between atoms and molecules and energy, we can better understand the world around us and develop new technologies.
Bonding
Bonding is a key aspect of the structure and properties of atoms and molecules. The type of bond that is formed between two atoms depends on the electronegativity of the atoms involved. Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself. Atoms with a high electronegativity will tend to form ionic bonds with atoms with a low electronegativity, while atoms with a similar electronegativity will tend to form covalent bonds.
- Covalent Bonds: Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. Covalent bonds are the strongest type of chemical bond and are found in many molecules, such as water, carbon dioxide, and methane.
- Ionic Bonds: Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom. Ionic bonds are found in many compounds, such as sodium chloride and potassium chloride.
- Hydrogen Bonds: Hydrogen bonds are formed between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, such as oxygen or nitrogen. Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds and ionic bonds, but they can play an important role in the structure and properties of many molecules, such as water and proteins.
The type of bond that is formed between two atoms has a significant impact on the properties of the resulting molecule. For example, covalent bonds are typically stronger than ionic bonds, and molecules with covalent bonds are typically more stable than molecules with ionic bonds. Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds and ionic bonds, but they can play an important role in the structure and properties of many molecules.
Understanding the different types of bonds that can form between atoms is essential for understanding the structure and properties of matter.
Polarity
The polarity of atoms and molecules is an important concept in chemistry. Polarity refers to the separation of charge within a molecule. A molecule is polar if it has a positive end and a negative end. Nonpolar molecules have no separation of charge.
- Electronegativity
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons. The more electronegative an atom is, the more strongly it attracts electrons. When two atoms with different electronegativities bond, the more electronegative atom will pull electrons away from the less electronegative atom. This creates a separation of charge, resulting in a polar bond.
- Molecular Shape
The shape of a molecule also affects its polarity. A molecule with a symmetrical shape, such as carbon dioxide, is nonpolar. This is because the electrons are evenly distributed around the molecule. A molecule with an asymmetrical shape, such as water, is polar. This is because the electrons are not evenly distributed around the molecule, resulting in a separation of charge.
- Dipole Moment
The dipole moment is a measure of the polarity of a molecule. The dipole moment is a vector that points from the positive end of the molecule to the negative end. The magnitude of the dipole moment is equal to the separation of charge multiplied by the distance between the charges.
- Examples
Polar molecules include water, ammonia, and hydrogen chloride. Nonpolar molecules include methane, carbon dioxide, and benzene.
The polarity of atoms and molecules has a significant impact on their properties. Polar molecules are more likely to dissolve in water than nonpolar molecules. Polar molecules also have higher boiling points than nonpolar molecules. The polarity of molecules is an important factor to consider when designing new materials and drugs.
Applications
Atoms and molecules are the basic building blocks of all matter, and understanding their properties and interactions is essential for developing new technologies and improving our understanding of the world around us.
- Energy Production
Atoms and molecules are used in a variety of energy production technologies, including nuclear power plants, solar cells, and fuel cells. Nuclear power plants use the energy released from the splitting of atoms to generate electricity. Solar cells use the energy of sunlight to generate electricity. Fuel cells use the energy released from the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to generate electricity.
- Medicine
Atoms and molecules are used in a variety of medical applications, including medical imaging, drug development, and gene therapy. Medical imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans use atoms and molecules to create images of the inside of the body. Drug development involves the use of atoms and molecules to create new drugs to treat diseases. Gene therapy involves the use of atoms and molecules to repair or replace damaged genes.
- Materials Science
Atoms and molecules are used in a variety of materials science applications, including the development of new materials for use in electronics, construction, and transportation. The development of new materials for use in electronics involves the use of atoms and molecules to create new materials with improved electrical and optical properties. The development of new materials for use in construction involves the use of atoms and molecules to create new materials with improved strength and durability. The development of new materials for use in transportation involves the use of atoms and molecules to create new materials with improved fuel efficiency and emissions.
These are just a few examples of the many ways that atoms and molecules are used in a wide variety of applications. By understanding the properties and interactions of atoms and molecules, we can continue to develop new technologies and improve our understanding of the world around us.
Frequently Asked Questions about Atoms and Molecules
This section provides answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about atoms and molecules.
Question 1: What are atoms and molecules?
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. They are composed of a nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, and electrons, which orbit the nucleus. Molecules are formed when two or more atoms are chemically bonded together.
Question 2: What are the different types of atoms and molecules?
There are many different types of atoms and molecules. Some of the most common atoms include hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen. Some of the most common molecules include water, carbon dioxide, and methane.
Question 3: What are the properties of atoms and molecules?
The properties of atoms and molecules are determined by the number and arrangement of their constituent particles. For example, the number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, which in turn determines its chemical properties.
Question 4: How do atoms and molecules interact with each other?
Atoms and molecules can interact with each other through a variety of forces, including covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds. These forces determine the structure and properties of matter.
Question 5: What are the applications of atoms and molecules?
Atoms and molecules are used in a wide variety of applications, including energy production, medicine, and materials science. For example, atoms and molecules are used in nuclear power plants, solar cells, and fuel cells to generate electricity.
Question 6: What are some of the challenges in studying atoms and molecules?
One of the challenges in studying atoms and molecules is their small size. Atoms and molecules are so small that they cannot be seen with a microscope. Another challenge is that atoms and molecules are constantly moving. This makes it difficult to study their structure and properties.
Despite these challenges, scientists have made great progress in understanding atoms and molecules. This understanding has led to the development of new technologies and a better understanding of the world around us.
These are just a few of the many questions that are commonly asked about atoms and molecules. By understanding the answers to these questions, we can gain a better understanding of the world around us.
To learn more about atoms and molecules, you can consult a variety of resources, including textbooks, websites, and scientific journals.
Conclusin
Los tomos y las molculas son los componentes bsicos de toda la materia en el universo. Son esenciales para la vida y desempean un papel vital en muchos procesos diferentes en nuestros cuerpos y en el mundo que nos rodea. Este artculo ha brindado una descripcin general de los conceptos clave relacionados con los tomos y las molculas, incluidos su estructura, propiedades, reactividad, energa, enlaces, polaridad y aplicaciones.
El estudio de los tomos y las molculas es un campo vasto y complejo, pero tambin es fascinante. Al comprender los tomos y las molculas, podemos comprender mejor el mundo que nos rodea y desarrollar nuevas tecnologas que mejoren nuestras vidas.
Uncover The Historic Appearance Of Betty White On Saturday Night Live
Professional Orlando Electricians You Can Trust
Explore The Perfect Behr Paint Color For Your Home's Personality

Definición de Molécula; ejemplos, y estructura (enlaces, y átomos)
Ser vivo Resultante interacción genomaambiente ATOMOS Y MOLECULAS

El átomo Diferencia entre átomo y molécula clases escolares